HIV Infection: Treatment Options and Symptoms Explained
During its earliest stage, stage one, most HIV symptoms are similar to what you might experience with the flu, allergies, or the common cold. Typically, they come on between two weeks and two months after transmission, and not everyone experiences all of the same symptoms. Some people may not experience any symptoms at all. That’s why, if you believe you’re at risk, it’s important to monitor any changes in your body and get tested as soon as possible.

Understanding HIV: Treatment Options and Symptoms Unveiled
HIV, or Human Immunodeficiency Virus, is a significant global health concern. Despite its complexity, understanding its symptoms and treatment options can help manage the disease and enhance quality of life. This article will delve into these aspects and shed light on the differences between HIV-1 and HIV-2.
What Is HIV?
HIV is a virus that attacks the immune system, specifically the CD4 cells, which help the body fight off infections. If left untreated, HIV can lead to AIDS (Acquired Immunodeficiency Syndrome), a severe condition where the immune system is so damaged that it can’t fight off disease and infection.
HIV-1 Vs. HIV-2: What’s the Difference?
While both types of HIV damage the immune system, there are significant differences. HIV-1 is the most common and widespread type, responsible for the majority of HIV infections worldwide. HIV-2, on the other hand, is less transmissible and primarily found in West Africa. The treatments for both types are similar, but some antiretroviral drugs used for HIV-1 are not effective against HIV-2.
How Does HIV-1 Spread?
HIV-1 primarily spreads through sexual contact, sharing injection drug equipment, and from mother to child during birth or breastfeeding. It’s important to note that HIV does not spread through casual contact, like shaking hands or sharing a meal.
Recognizing the Early Warning Signs of HIV-1
Early HIV symptoms often resemble the flu, including fever, fatigue, and body aches. These might occur two weeks to two months after transmission. However, some people may not experience any symptoms at all initially. Hence, regular testing is crucial if you’re at risk.
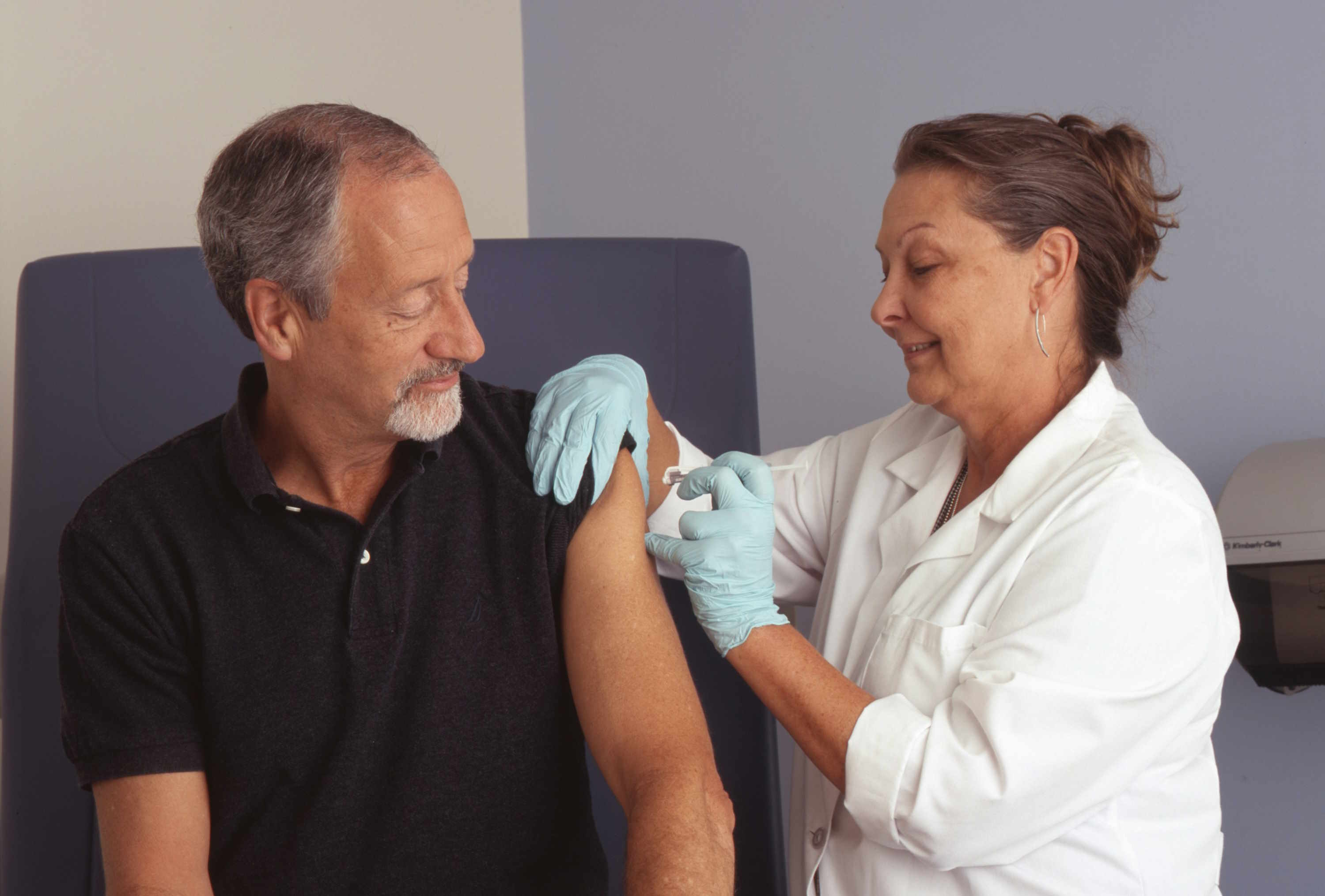
Treatment Options for HIV-1
Antiretroviral therapy (ART) is the standard treatment for HIV. It involves taking a combination of HIV medicines daily to control the virus’s spread and prevent progression to AIDS. ART also reduces the risk of HIV transmission.
Navigating HIV Treatment in the United States
In the USA, several organizations and programs provide HIV treatment services. Here’s a comparison of four such providers:
| Provider | Services | Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| AIDS Healthcare Foundation | Medical care, pharmacy services, preventive education | Nationwide services, free HIV testing |
| Ryan White HIV/AIDS Program | Primary medical care, essential support services | Serves low-income individuals without sufficient healthcare coverage |
| SAMHSA | Substance abuse and mental health services | Offers grants for HIV treatment |
| CDC | Prevention resources, testing, linkage to care | Comprehensive approach to combat HIV |
Choosing a provider might depend on various factors, including the services offered, accessibility, and any associated costs. Remember, the information provided here is estimated. It’s crucial to do independent research to find the most suitable and cost-effective service.
Understanding HIV, its symptoms, and treatment options is vital for anyone living with the virus or at risk of infection. With advancements in medical science, HIV can be managed effectively, and people with the virus can lead a healthy life. So, stay informed, get tested, and seek treatment promptly if needed.