The Early Signs And Symptoms Of Breast Cancer
Breast cancer is one of the most commonly discussed health conditions, making early awareness especially important. This article explains how breast cancer develops, outlines common early signs and symptoms, and reviews current diagnostic approaches. It also provides an overview of modern treatment options, including therapies for HER2 positive breast cancer, along with practical facts that help readers better understand ongoing research and future directions in breast cancer care.

This article is for informational purposes only and should not be considered medical advice. Please consult a qualified healthcare professional for personalized guidance and treatment.
Understanding Breast Cancer
Breast cancer originates when cells in the breast grow out of control, forming a tumor that can often be felt as a lump. While it is more common in women, men can also develop breast cancer. The disease can begin in different parts of the breast, most commonly in the milk ducts (ductal carcinomas) or the lobules (lobular carcinomas). Understanding the basic biology of breast cancer, including its various types and risk factors, is foundational for grasping the importance of early detection. Factors such as genetics, age, lifestyle choices, and exposure to certain environmental elements can influence an individual’s risk.
Key Early Signs and Symptoms
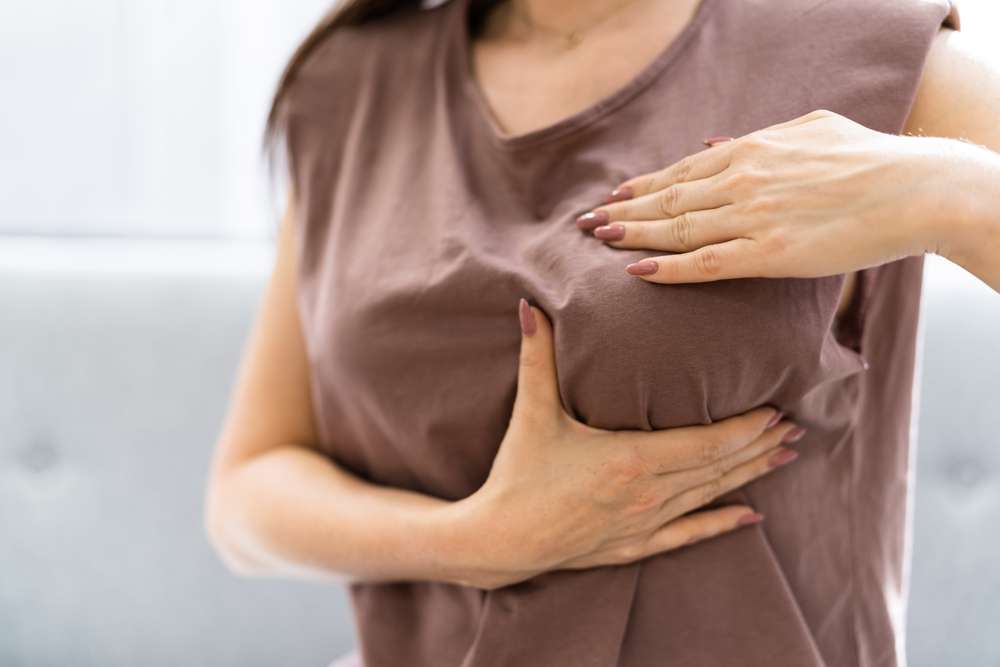
Recognizing the early signs and symptoms of breast cancer is paramount for early intervention. The most common symptom is a new lump or mass in the breast, which may feel different from the surrounding tissue. However, not all lumps are cancerous, and many are benign. Other potential indicators include changes in the size or shape of the breast, nipple discharge (other than breast milk), nipple inversion or tenderness, and skin changes such as dimpling, puckering, redness, or scaling on the breast or nipple. Swelling of all or part of a breast, even if no distinct lump is felt, should also prompt medical evaluation. Pain in the breast or nipple, while less common as an initial symptom of cancer, should not be ignored, particularly if persistent. Being vigilant about these changes and consulting a healthcare provider promptly is a critical step in managing breast health.
Modern Treatment Approaches for HER2-Positive Breast Cancer
HER2-positive breast cancer is a type that tests positive for a protein called human epidermal growth factor receptor 2, which promotes the growth of cancer cells. Modern treatment strategies for HER2-positive breast cancer often involve targeted therapies that specifically block the HER2 protein, alongside traditional chemotherapy. Medications like trastuzumab and pertuzumab have revolutionized the prognosis for individuals with this subtype, significantly improving outcomes. These treatments work by inhibiting the growth signals that fuel HER2-positive cancer cells, making them less aggressive and more responsive to therapy. The development of such targeted agents represents a major advancement in personalized cancer care, tailoring interventions to the specific molecular characteristics of a tumor.
Useful Tips and Facts About Breast Cancer
Staying informed and proactive about breast health involves several useful tips and facts. Regular self-breast exams can help individuals become familiar with their breasts’ normal appearance and feel, making it easier to detect any changes. Clinical breast exams performed by a healthcare professional are also important. Mammograms remain the most effective screening tool for detecting breast cancer early, often before a lump can be felt. Current guidelines recommend regular mammograms for women starting at a certain age, typically 40 or 50, depending on individual risk factors and local services. Maintaining a healthy weight, limiting alcohol consumption, engaging in regular physical activity, and choosing a nutritious diet are lifestyle factors that can contribute to reducing breast cancer risk. Understanding one’s family history of breast cancer is also vital, as it can influence screening recommendations and risk assessment.
| Treatment Type | Description | Estimated Cost Range (USD) |
|---|---|---|
| Surgery (Lumpectomy/Mastectomy) | Removal of the tumor or the entire breast | $15,000 - $60,000+ |
| Chemotherapy | Drugs used to kill cancer cells, often administered intravenously | $10,000 - $100,000+ |
| Radiation Therapy | High-energy rays to kill cancer cells | $10,000 - $50,000+ |
| Targeted Therapy | Drugs that target specific cancer cells (e.g., HER2-positive) | $20,000 - $150,000+ annually |
| Hormone Therapy | Medications to block hormones that fuel cancer growth (e.g., estrogen) | $200 - $1,000+ monthly |
Prices, rates, or cost estimates mentioned in this article are based on the latest available information but may change over time. Independent research is advised before making financial decisions.
A Glimpse into the Future of Breast Cancer Treatment
The future of breast cancer treatment is evolving rapidly, with research focused on even more personalized and less invasive approaches. Advances in genomic sequencing are allowing for a deeper understanding of individual tumor characteristics, leading to the development of highly specific targeted therapies and immunotherapies. Immunotherapy, which harnesses the body’s own immune system to fight cancer, shows significant promise for certain subtypes. Liquid biopsies, a non-invasive blood test, are being explored for early detection, monitoring treatment effectiveness, and detecting recurrence. Furthermore, artificial intelligence and machine learning are being integrated into diagnostic tools and treatment planning, potentially leading to more accurate diagnoses and optimized patient care. These innovations aim to improve survival rates, reduce side effects, and enhance the overall quality of life for individuals affected by breast cancer.
In conclusion, understanding the early signs and symptoms of breast cancer is a cornerstone of effective health management. Coupled with knowledge about modern treatment options and ongoing research, individuals can take proactive steps towards early detection and informed decision-making regarding their health. Continued awareness, regular screenings, and a commitment to a healthy lifestyle remain vital in the ongoing effort to combat breast cancer.