Judicial Bypass: A Legal Lifeline for Minors Seeking Abortion
Introduction: In the complex landscape of reproductive rights, judicial bypass emerges as a critical legal mechanism. This process allows minors to obtain court approval for an abortion without parental consent, balancing the rights of young individuals with parental authority and state interests. As abortion laws continue to evolve, understanding judicial bypass becomes increasingly important for healthcare providers, legal professionals, and the public.
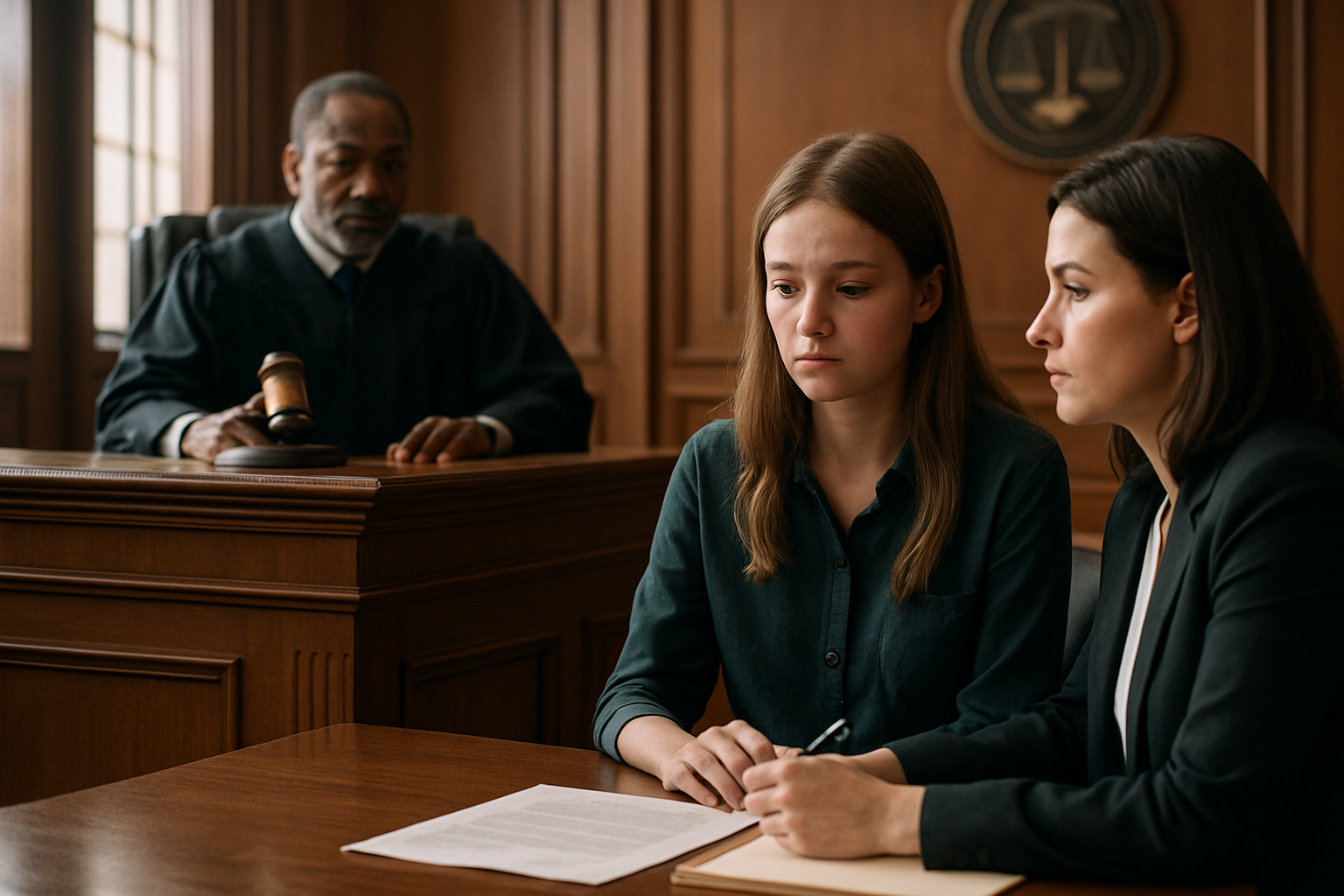

Since Bellotti, numerous states have implemented judicial bypass procedures, each with its own specific requirements and processes. These laws aim to strike a delicate balance between respecting parental rights, protecting minors, and upholding constitutional guarantees.
The Judicial Bypass Process
The judicial bypass procedure typically involves several steps. A minor seeking an abortion without parental consent must petition the court, often with the assistance of an attorney or legal advocate. The court then schedules a hearing, usually within a few days to ensure timeliness. During the hearing, a judge evaluates whether the minor is sufficiently mature and well-informed to make the decision independently or if the abortion is in her best interests.
Confidentiality is a crucial aspect of this process. Courts are required to ensure the minor’s identity remains protected throughout the proceedings. This confidentiality is essential to safeguard the minor from potential harm or retaliation.
Challenges and Criticisms
Despite its intended purpose, the judicial bypass system faces significant challenges and criticisms. Opponents argue that it undermines parental rights and may lead to hasty decisions by minors. They contend that parental involvement is crucial for the well-being of young individuals facing such a significant decision.
Conversely, supporters of judicial bypass argue that it provides a necessary safeguard for minors in difficult situations. They point out that for many young people, involving parents is simply not a safe or viable option due to factors such as abuse, incest, or severe family dysfunction.
Recent Legal Developments
In recent years, several states have sought to restrict or complicate the judicial bypass process. Some have introduced longer waiting periods, stricter venue requirements, or higher standards of proof for judges to grant approval. These changes have sparked legal challenges, with courts grappling to determine the constitutionality of such restrictions.
For example, in 2021, the Texas legislature passed a law requiring judges to assess whether a minor has been a victim of abuse or trafficking before granting a bypass. Critics argue that this additional requirement could deter vulnerable minors from seeking judicial bypass and potentially re-traumatize abuse survivors.
Impact on Minors and Society
The availability and accessibility of judicial bypass procedures have significant implications for minors facing unintended pregnancies. Research suggests that the majority of minors do involve at least one parent in their abortion decision. However, for those who cannot, judicial bypass serves as a crucial safety net.
The process can be emotionally taxing for young individuals, who must navigate a complex legal system while dealing with a time-sensitive and deeply personal issue. Advocates stress the importance of providing comprehensive support services, including counseling and legal assistance, to minors going through this process.
Future of Judicial Bypass
As the legal landscape surrounding abortion rights continues to shift, the future of judicial bypass remains uncertain. Some legal experts predict that restrictions on abortion access may lead to an increased reliance on judicial bypass procedures in states where they remain available.
Others speculate that changes in the composition of the Supreme Court could potentially lead to a reevaluation of the constitutional foundations of judicial bypass. This possibility underscores the need for ongoing legal scholarship and advocacy in this area.
Conclusion
Judicial bypass represents a complex intersection of reproductive rights, parental authority, and the state’s interest in protecting minors. As debates over abortion access continue to intensify, understanding the nuances of judicial bypass becomes increasingly crucial. Legal professionals, policymakers, and the public must grapple with balancing the rights and well-being of minors with broader societal concerns. The evolution of judicial bypass laws will undoubtedly play a significant role in shaping the future of reproductive rights for young individuals in the United States.