Aquatic Acrobats: The Surprising World of Jumping Fish
Imagine a serene lake or river suddenly erupting with fish leaping gracefully into the air. This isn't a scene from a fantasy novel, but a real phenomenon observed in various aquatic environments worldwide. From the iconic salmon's upstream journey to the lesser-known flying fish's aerial adventures, jumping fish have long captivated both scientists and nature enthusiasts. This article delves into the fascinating world of these aquatic acrobats, exploring the reasons behind their leaps, the species known for this behavior, and the impact of this ability on their survival and evolution.
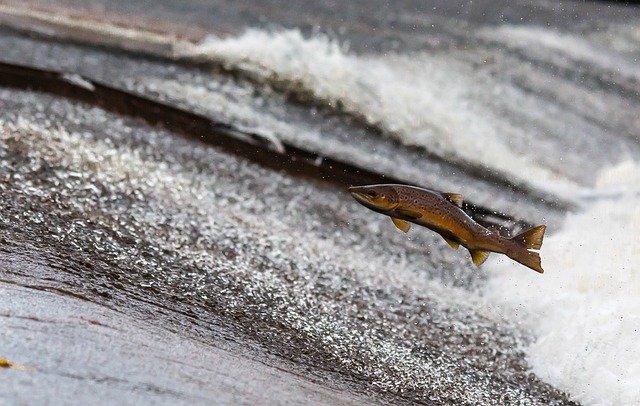

Another common reason for fish jumping is migration. Species like salmon are well-known for their impressive leaps up waterfalls and over obstacles as they journey to their spawning grounds. These jumps, often against strong currents, showcase the incredible strength and determination of these fish.
Notable Jumping Fish Species
While many fish species can jump, some are particularly renowned for their acrobatic abilities. The arapaima, native to the Amazon Basin, is one of the largest freshwater fish in the world and can leap up to 2 meters out of the water. This impressive feat helps them catch low-flying birds and bats for food.
The silver carp, an invasive species in North American waterways, has gained notoriety for its jumping behavior. These fish can leap up to 3 meters high when startled by boat engines, posing a safety risk to boaters and water-skiers.
Evolutionary Advantages of Jumping
The ability to jump has provided numerous evolutionary advantages to fish species. For some, like the mudskipper, jumping has enabled them to temporarily leave their aquatic environment and explore land. This adaptation has allowed them to access new food sources and escape aquatic predators.
In the case of flying fish, their remarkable gliding ability - an extension of jumping - helps them evade predators by covering distances of up to 50 meters in a single glide. This adaptation has significantly improved their chances of survival in open ocean environments.
Impact on Ecosystems and Human Activities
Jumping fish play crucial roles in their ecosystems. Salmon, for instance, transport marine nutrients inland during their spawning runs, benefiting terrestrial plants and animals. However, human activities like dam construction have created barriers to these natural migrations, necessitating the development of fish ladders and other passage systems.
The behavior of jumping fish also impacts human activities. In some regions, fishermen have developed techniques to catch fish mid-jump, while in others, jumping fish pose challenges for aquaculture operations and recreational water activities.
Conservation Implications
As with many aspects of nature, human activities are impacting the habitats and behaviors of jumping fish. Water pollution, overfishing, and climate change are altering aquatic environments, potentially affecting the ability of fish to perform these crucial jumps.
Conservation efforts are underway to protect species known for their jumping behavior. These include habitat restoration projects, the removal or modification of dams to allow fish passage, and regulations to control invasive jumping species like the silver carp.
Understanding the behavior of jumping fish not only satisfies our curiosity about the natural world but also provides valuable insights for conservation efforts and ecosystem management. As we continue to study these aquatic acrobats, we may uncover even more surprising adaptations and behaviors, reminding us of the endless wonders that exist beneath the water’s surface.