The Resurgence of Hydrogen Fuel Cell Vehicles
In a world increasingly focused on sustainable transportation, hydrogen fuel cell vehicles (FCVs) are making a surprising comeback. Once considered a niche technology, FCVs are now gaining traction as a viable alternative to traditional combustion engines and battery electric vehicles. This article delves into the renewed interest in hydrogen-powered cars, exploring the technology's potential to revolutionize the automotive industry and address key environmental concerns.
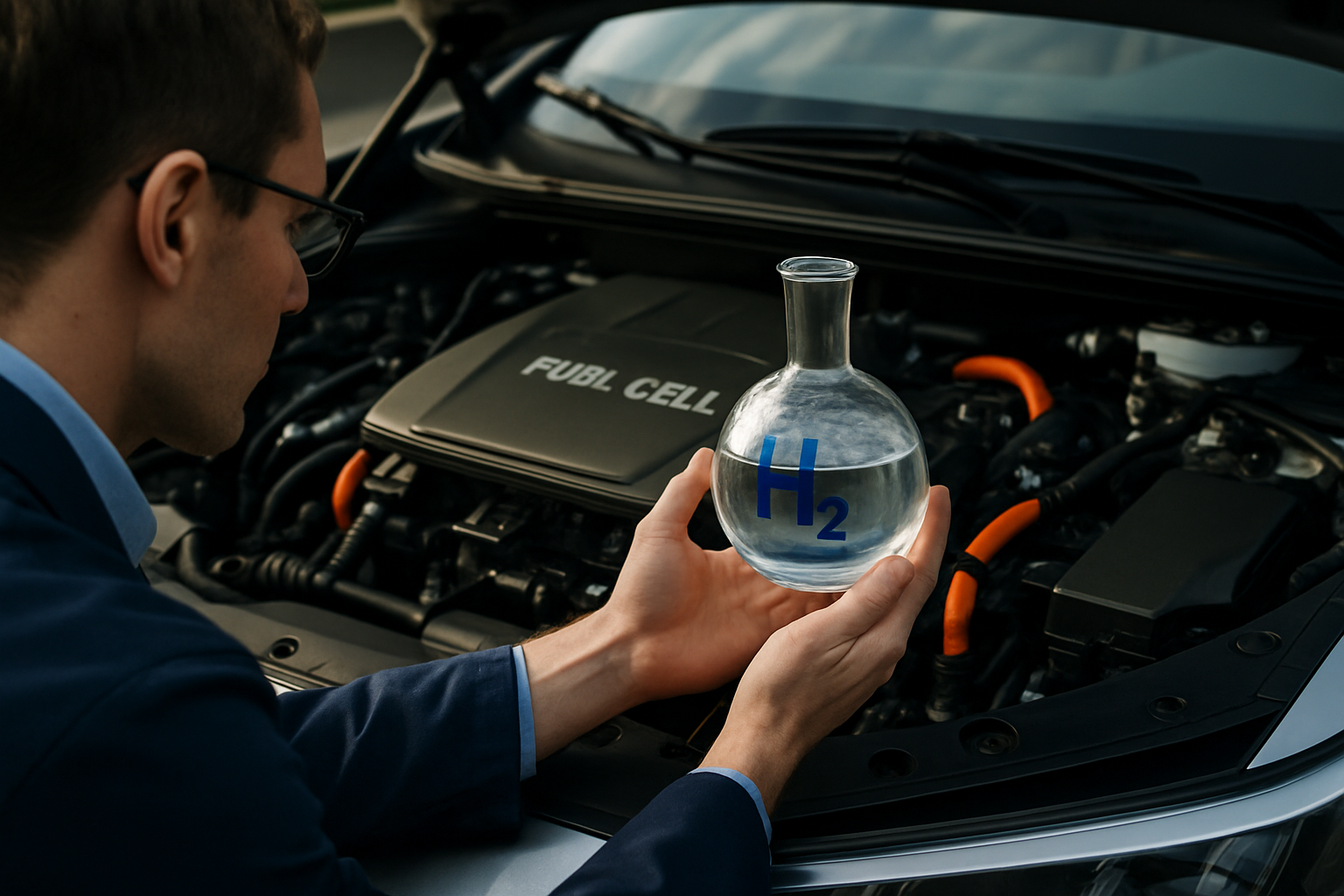

The Science Behind Hydrogen Fuel Cells
At the heart of hydrogen fuel cell vehicles lies a complex yet elegant system that converts chemical energy into electrical power. Fuel cells combine hydrogen from on-board tanks with oxygen from the air to produce electricity, with water vapor as the only byproduct. This process, known as electrolysis in reverse, is both clean and efficient, offering a stark contrast to the carbon-intensive nature of traditional internal combustion engines.
The fuel cell stack, composed of multiple individual cells, generates the electricity needed to power the vehicle’s electric motor. This setup allows for a driving experience similar to that of battery electric vehicles, with instant torque and smooth acceleration. However, unlike battery-powered cars, FCVs can be refueled in a matter of minutes, addressing one of the main concerns associated with electric vehicles – long charging times.
Infrastructure Challenges and Solutions
One of the primary obstacles to widespread adoption of hydrogen FCVs has been the lack of refueling infrastructure. Unlike gasoline stations, which are ubiquitous in most countries, hydrogen fueling stations are still relatively scarce. This chicken-and-egg problem has hindered both consumer interest and manufacturer investment in the technology.
However, recent years have seen a concerted effort to expand hydrogen infrastructure. Countries like Japan, Germany, and South Korea are leading the charge, investing heavily in the development of hydrogen fueling networks. In the United States, California has been at the forefront of hydrogen infrastructure development, with plans to have 200 stations operational by 2025. These initiatives are crucial in creating the foundation for a hydrogen-based transportation ecosystem.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
The environmental credentials of hydrogen fuel cell vehicles are a major driving force behind their resurgence. When powered by green hydrogen – produced using renewable energy sources – FCVs offer a truly zero-emission solution from well to wheel. This potential for complete decarbonization of the transportation sector is particularly appealing in the face of increasingly stringent emissions regulations worldwide.
Moreover, hydrogen production can serve as a form of energy storage, helping to balance the intermittent nature of renewable energy sources like wind and solar. Excess electricity generated during peak production periods can be used to produce hydrogen through electrolysis, which can then be stored and used later in fuel cell vehicles or other applications. This synergy between renewable energy and hydrogen production creates a more resilient and sustainable energy ecosystem.
Technological Advancements and Cost Reduction
Recent technological breakthroughs have significantly improved the performance and reduced the cost of fuel cell systems. Innovations in catalyst materials, such as the use of platinum nanoparticles, have increased efficiency while decreasing the amount of precious metals required. This not only improves the economic viability of FCVs but also addresses concerns about the sustainability of resource extraction.
Additionally, advancements in hydrogen storage technology have increased the range of FCVs, with some models now capable of traveling over 400 miles on a single tank. Coupled with the quick refueling times, this extended range makes hydrogen FCVs an increasingly practical option for long-distance travel and commercial applications.
Industry Collaboration and Government Support
The revival of hydrogen fuel cell technology has been marked by unprecedented collaboration between automakers, energy companies, and governments. Joint ventures and partnerships are becoming commonplace as industry players pool resources and expertise to overcome technical challenges and develop standardized solutions.
Government support has also played a crucial role in the resurgence of FCVs. Many countries have implemented incentives and subsidies to encourage the adoption of hydrogen-powered vehicles, similar to those offered for battery electric vehicles. These policies not only make FCVs more affordable for consumers but also signal long-term commitment to the technology, encouraging further investment and development.
The Future of Hydrogen in Transportation
As the automotive industry continues to evolve, hydrogen fuel cell vehicles are poised to play an increasingly important role in the transition to sustainable transportation. While they may not replace battery electric vehicles entirely, FCVs offer a complementary solution that addresses some of the limitations of battery technology, particularly for heavy-duty vehicles and long-distance transportation.
The coming years will likely see a diversification of the automotive market, with different technologies coexisting to meet varied transportation needs. Hydrogen FCVs, with their quick refueling times, long range, and zero-emission operation, are well-positioned to carve out a significant niche in this new landscape.
In conclusion, the resurgence of hydrogen fuel cell vehicles represents a promising development in the quest for sustainable transportation. As technology advances, infrastructure expands, and costs decrease, we may well be witnessing the dawn of a hydrogen-powered future on our roads. The journey ahead is still long, but the potential rewards – both for the environment and for the automotive industry – make it a path worth pursuing.